India Business Information
Business India
Visitors: 1727
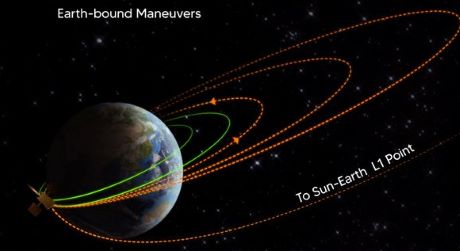
India's first solar observatory mission Aditya-L1
What is Aditya L1?
Aditya L1 shall be the first space based Indian mission to study the Sun. The spacecraft shall be placed in a halo orbit around the Lagrange point 1 (L1) of the Sun-Earth system, which is about 1.5 million km from the Earth. A satellite placed in the halo orbit around the L1 point has the major advantage of continuously viewing the Sun without any occultation/eclipses. This will provide a greater advantage of observing the solar activities and its effect on space weather in real time. The spacecraft carries seven payloads to observe the photosphere, chromosphere and the outermost layers of the Sun (the corona) using electromagnetic and particle and magnetic field detectors. Using the special vantage point L1, four payloads directly view the Sun and the remaining three payloads carry out in-situ studies of particles and fields at the Lagrange point L1, thus providing important scientific studies of the propagatory effect of solar dynamics in the interplanetary mediumThe suits of Aditya L1 payloads are expected to provide most crucial informations to understand the problem of coronal heating, coronal mass ejection, pre-flare and flare activities and their characteristics, dynamics of space weather, propagation of particle and fields etc.
Aditya-L1 Mission:
POST from X : ISRO@isro on Sep 15, 2023 2:29 AMThe fourth Earth-bound maneuvre (EBN#4) is performed successfully.

ISRO's ground stations at Mauritius, Bengaluru, SDSC-SHAR and Port Blair tracked the satellite during this operation, while a transportable terminal currently stationed in the Fiji islands for Aditya-L1 will support post-burn operations.
The new orbit attained is 256 km x 121973 km.
The next maneuvre Trans-Lagragean Point 1 Insertion (TL1I) -- a send-off from the Earth -- is scheduled for September 19, 2023, around 02:00 Hrs. IST
Aditya-L1 Mission:
POST from X : ISRO@isro on Sep 5, 2023 3:00 AMThe second Earth-bound maneuvre (EBN#2) is performed successfully from ISTRAC, Bengaluru.
ISTRAC/ISRO's ground stations at Mauritius, Bengaluru and Port Blair tracked the satellite during this operation.
The new orbit attained is 282 km x 40225 km.
The next maneuvre (EBN#3) is scheduled for September 10, 2023, around 02:30 Hrs. IST
What is Aditya L1?
Aditya L1 shall be the first space based Indian mission to study the Sun. The spacecraft shall be placed in a halo orbit around the Lagrange point 1 (L1) of the Sun-Earth system, which is about 1.5 million km from the Earth. A satellite placed in the halo orbit around the L1 point has the major advantage of continuously viewing the Sun without any occultation/eclipses. This will provide a greater advantage of observing the solar activities and its effect on space weather in real time. The spacecraft carries seven payloads to observe the photosphere, chromosphere and the outermost layers of the Sun (the corona) using electromagnetic and particle and magnetic field detectors. Using the special vantage point L1, four payloads directly view the Sun and the remaining three payloads carry out in-situ studies of particles and fields at the Lagrange point L1, thus providing important scientific studies of the propagatory effect of solar dynamics in the interplanetary mediumThe suits of Aditya L1 payloads are expected to provide most crucial informations to understand the problem of coronal heating, coronal mass ejection, pre-flare and flare activities and their characteristics, dynamics of space weather, propagation of particle and fields etc.
What is Aditya-L1 launch date?
2nd September 2023It is the first Indian mission dedicated to observing the Sun. Nigar Shaji is the project's director. It was launched aboard a PSLV-XL launch vehicle at 11:50 IST on 2nd September 2023, ten days after the successful landing of ISRO's moon mission, Chandrayaan 3.
The Cost of Aditya L1 is 5.5 CR USD
Science Objectives:
The major science objectives of Aditya-L1 mission are:
Study of Solar upper atmospheric (chromosphere and corona) dynamics.
Study of chromospheric and coronal heating, physics of the partially ionized plasma, initiation of the coronal mass ejections, and flares
Observe the in-situ particle and plasma environment providing data for the study of particle dynamics from the Sun.
Physics of solar corona and its heating mechanism.
Diagnostics of the coronal and coronal loops plasma: Temperature, velocity and density.
Development, dynamics and origin of CMEs.
Identify the sequence of processes that occur at multiple layers (chromosphere, base and extended corona) which eventually leads to solar eruptive events.
Magnetic field topology and magnetic field measurements in the solar corona .
Drivers for space weather (origin, composition and dynamics of solar wind .
Science Objectives:
The major science objectives of Aditya-L1 mission are:
Study of Solar upper atmospheric (chromosphere and corona) dynamics.
Study of chromospheric and coronal heating, physics of the partially ionized plasma, initiation of the coronal mass ejections, and flares
Observe the in-situ particle and plasma environment providing data for the study of particle dynamics from the Sun.
Physics of solar corona and its heating mechanism.
Diagnostics of the coronal and coronal loops plasma: Temperature, velocity and density.
Development, dynamics and origin of CMEs.
Identify the sequence of processes that occur at multiple layers (chromosphere, base and extended corona) which eventually leads to solar eruptive events.
Magnetic field topology and magnetic field measurements in the solar corona .
Drivers for space weather (origin, composition and dynamics of solar wind .
Aditya-L1 Payloads
The instruments of Aditya-L1 are tuned to observe the solar atmosphere mainly the chromosphere and corona. In-situ instruments will observe the local environment at L1. There are total seven payloads on-board with four of them carrying out remote sensing of the Sun and three of them carrying in-situ observation.1. VELC - Visible Emission Line Coronagraph
2. SUIT - Solar Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope
3. SoLEXS - Solar Low Energy X-ray Spectrometer
4. HEL1OS - High Energy L1 Orbiting X-ray Spectrometer
5. ASPEX - Aditya Solar wind Particle Experiment
6. PAPA - Plasma Analyser Package For Aditya
7. Advanced Tri-axial High Resolution Digital Magnetometers
Popular Post(s)...
/Sports
/Online Shopping
/Online Shopping
/Online Shopping
/Sports
Menu
- IPL
- World University rankings 2022, 2023
- Weight Loss
- Website Monetization
- United States Free Business Directory
- Tech Support
- Study in US
- Study in United Kingdom
- Study in India
- Sports
- Pets Name
- Movie and Theatres
- London Business Directory
- Aadhaar Services
- Indian Food Recipes
- Home
- American Food Recipes
- Astrology
- Best Hits Of Madhuri Dixit
- Bollywood Celebrities
- Business India
- Corona News
- DTDC Courier Tracking
- Ecom Express Tracking
- Fully Funded UK Scholarships
- Hit Video Songs
- India Track Your Courier
- States-and-Capitals
- Tamilnadu-Business
- Currency Exchange
- Online Shopping
- Baby Names by Birth Star
 ( 5 ) by 1 User(s).
( 5 ) by 1 User(s).